The Volatility Index (VIX), often referred to as the “fear gauge,” is a powerful tool for traders seeking to understand market sentiment and manage risk. This article delves into the concept of the VIX, explaining its significance in trading, and provides actionable strategies to help traders navigate market fluctuations effectively. Whether you are an experienced trader or just starting, this guide will offer insights into using the VIX for better risk management in your trading decisions.
Understanding the VIX
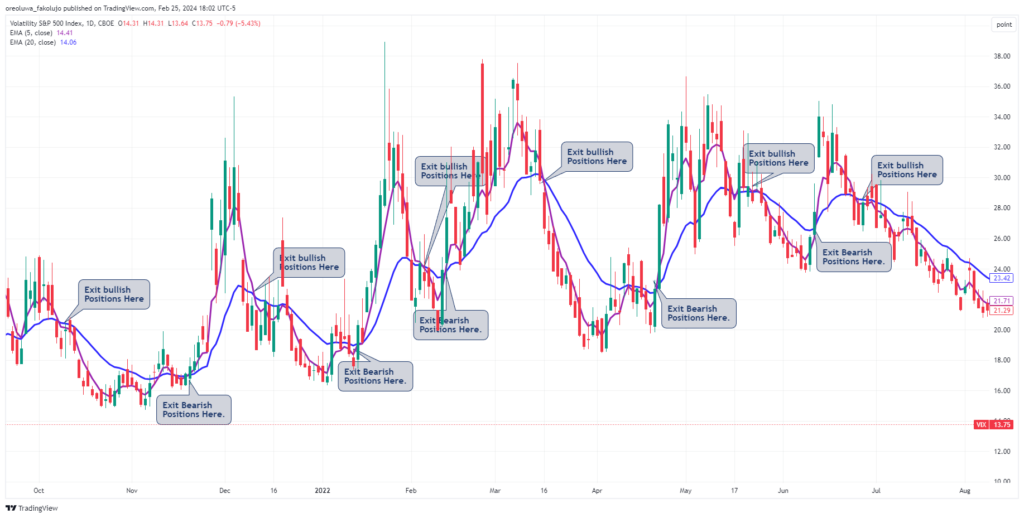
The VIX is a market index designed to measure the expected volatility in the S&P 500 index over the next 30 days, based on the prices of options. In essence, it reflects the level of uncertainty or fear in the market. When the VIX is high, it suggests that investors anticipate significant price fluctuations, often due to market stress or economic uncertainty. Conversely, a low VIX indicates a calm market, with expectations of stable price movements.
The VIX is calculated using the prices of S&P 500 options, specifically looking at the implied volatility, which reflects the market’s expectations of future price movement. The higher the implied volatility in the options market, the higher the VIX reading. Traders use the VIX to gauge market sentiment—whether fear or complacency is driving the market—and to make informed decisions about their trades.
For those wondering, “Can you trade the VIX?” the answer is yes. Traders can use various instruments like VIX futures, options, ETFs, and ETNs to gain exposure to volatility, making it a versatile tool for managing risk and capitalizing on market sentiment.
Importance of the VIX in Risk Management
The VIX serves as an essential tool for managing risk in any trading strategy. As a leading indicator, it provides valuable insight into market psychology, often signalling impending shifts in market direction. When the VIX rises sharply, it usually indicates increased uncertainty or fear among investors, suggesting that a potential market downturn may be imminent. Conversely, when the VIX falls, it may signal confidence and the possibility of a stable or rising market.
By monitoring the VIX, traders can anticipate and prepare for market movements, allowing them to hedge their positions or adjust their strategies to protect against potential losses. A sudden spike in the VIX could signal a correction or market crash, providing an opportunity to exit long positions or even enter short positions. This level of awareness allows traders to make more informed, risk-adjusted decisions.
Additionally, the VIX is often used in conjunction with other indicators to enhance risk management. For example, pairing VIX movements with technical analysis or macroeconomic data can help confirm or contradict market trends, giving traders more confidence in their decisions.
Popular VIX Trading Strategies
There are several strategies that traders employ when using the VIX for risk management, each suited to different market conditions and risk profiles. One common approach is using VIX futures and options to hedge against volatility. These derivative products allow traders to take positions on the future movement of the VIX itself, providing a way to profit from rising volatility while hedging existing equity positions.
VIX futures work by locking in a price for the VIX at a future date, allowing traders to gain exposure to volatility without directly trading the underlying assets. Similarly, VIX options give traders the right—but not the obligation—to buy or sell VIX futures at a predetermined price, offering flexibility and leverage. By incorporating VIX futures or options into a portfolio, traders can protect themselves from large losses during periods of heightened volatility.
Another strategy involves taking long or short positions based on the VIX itself. When volatility is expected to rise, traders may take long positions in VIX-related products, such as VIX ETFs or options, anticipating an increase in volatility. Conversely, during periods of low volatility, traders might short VIX-related instruments, betting that the index will fall as the market stabilizes. Understanding the relationship between the VIX and market sentiment is crucial for timing these trades effectively.
Practical Steps to Trade Using the VIX
To begin trading with the VIX, the first step is to ensure you have the right tools and data sources. Access to real-time VIX data is crucial for monitoring shifts in market sentiment. Many trading platforms offer built-in VIX tracking, but for more advanced analysis, you may want to consider subscribing to specialized data services.
Once you have the necessary tools, it’s time to integrate technical analysis into your VIX trading strategy. Various indicators, such as moving averages and Bollinger Bands, can help you identify patterns and potential trends in the VIX. For example, when the VIX approaches the upper band of a Bollinger Band, it may signal an overbought condition, indicating that the market is primed for a reversal.
Conclusion
The VIX is a vital tool for traders looking to manage risk and navigate the complexities of market volatility. By understanding how the VIX works, interpreting its signals, and employing effective trading strategies, traders can protect themselves from unforeseen market swings and capitalize on potential opportunities. Whether using the VIX for hedging, market timing, or volatility-based trades, incorporating it into your trading strategy will enhance your ability to make informed, risk-adjusted decisions.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/midsection-businessmen-analyzing-charts-on-laptop-in-office-1128046391-4d6016296f824cd48bf762d5824e49e4.jpg)









